Leader-Follower Replication in Databases: Simplified
Leader-follower replication is a widely-used approach for ensuring data availability and redundancy in distributed databases. It's designed to replicate data from one primary (leader) node to multiple secondary (follower) nodes. This architecture helps improve system performance, scalability, and reliability.
Let’s break it down:
How Leader-Follower Replication Works
-
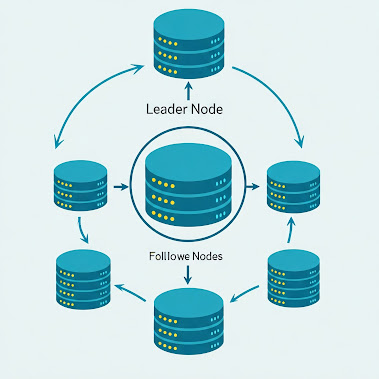
Leader Node
- The leader node handles all write operations (inserts, updates, deletes).
- It’s the single source of truth for the database.
-
Follower Nodes
- Follower nodes replicate data from the leader, typically in real-time or near real-time.
- They handle read operations, reducing the load on the leader.
Key Benefits
-
Scalability:
By offloading reads to followers, the system can handle a larger number of read requests. -
Fault Tolerance:
In case the leader fails, one of the followers can be promoted to act as the new leader. -
Improved Performance:
Distributing the read workload across followers minimizes latency for end-users.
Challenges
-
Data Consistency:
Followers replicate data asynchronously, so they may lag behind the leader. This can lead to eventual consistency rather than strong consistency. -
Write Bottleneck:
Since all write operations go through the leader, it can become a bottleneck if the system has high write demands. -
Failover Complexity:
Promoting a follower to leader during a failure requires careful orchestration to avoid downtime or data conflicts.
Real-Life Example
Imagine an e-commerce platform:
- The leader node processes all new orders (writes).
- The followers handle product searches, customer reviews, or browsing history (reads).
This setup ensures that write-heavy operations like placing orders don’t slow down the user experience for those browsing products.
Diagram
Here’s a simple representation of leader-follower replication:
Write Requests
↓
Leader Node
↓
-------------------------
| |
Follower 1 Follower 2
| |
Read Requests Read Requests
When to Use Leader-Follower Replication
- Read-heavy applications: Like news sites or social media feeds, where there are far more reads than writes.
- Fault-tolerant systems: Where downtime is unacceptable, and failover mechanisms are critical.
- Scalable architectures: When the system must handle growing user demands seamlessly.
Conclusion
Leader-follower replication is an essential technique for building scalable, reliable, and high-performing distributed systems. While it comes with challenges, it’s a proven solution for balancing workloads and ensuring data availability. Understanding its trade-offs and implementation nuances is key to leveraging it effectively in real-world applications.
Written by Sunny, aka Engineerhoon — simplifying tech, one blog at a time!

Comments
Post a Comment